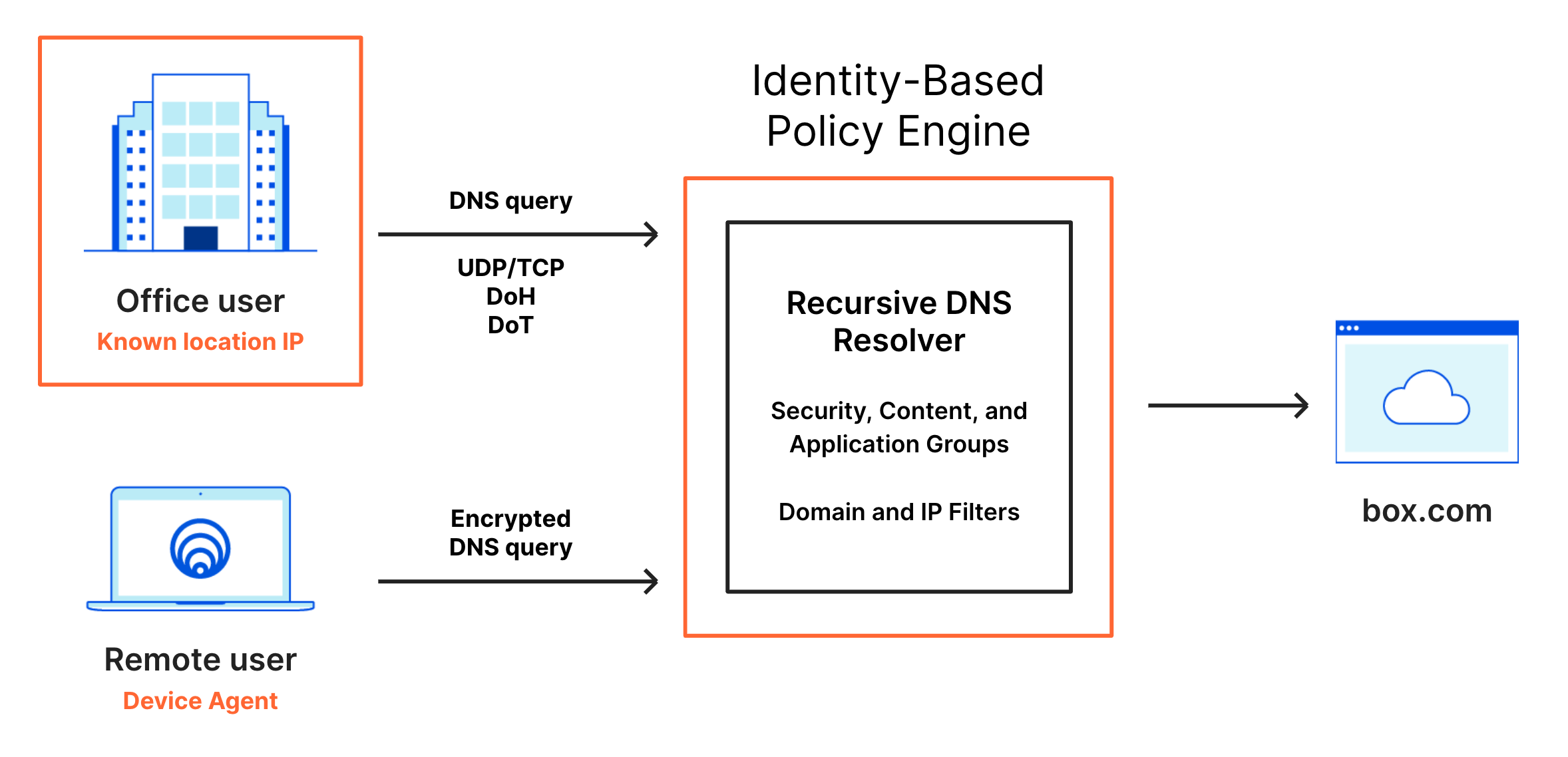
DNS policies
When a user makes a DNS request to Gateway, Gateway matches the request against the content or security categories you have set up for your organization. If the domain does not belong to any blocked categories, or if it matches an Override policy, the user’s client receives the DNS resolution and initiates an HTTP connection.
When creating a DNS policy, you can select as many security risk categories and content categories as needed to fully secure your network.
Build a DNS policy by configuring the following elements:
Expressions
Build expressions to determine the set of elements you want to impact with your policy. To build an expression, you need to choose a Selector and an Operator, and enter a value or range of values in the Value field.
Selectors
Gateway matches DNS traffic against the following selectors, or criteria:
Identity-based selectors
You can build DNS policies using identity-based selectors. These selectors require Gateway with WARP mode to be enabled in the Zero Trust WARP client and the user to be enrolled in the organization via the WARP client. For a list of identity-based selectors and API examples, please refer to the dedicated section .
DOH Subdomain
Use this selector to match against DNS queries that arrive via DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) destined for the DoH endpoint configured for each location. For example, a location with a DoH endpoint of abcdefg.cloudflare-gateway.com could be used in a DNS rule by choosing the DoH Subdomain selector and inputting a value of abcdefg.
| UI name | API example |
|---|---|
| DOH Subdomain | dns.doh_subdomain == "abcdefg" |
Domain
Use this selector to match against a domain and all subdomains — for example, if you want to block example.com and all subdomains of example.com.
| UI name | API example |
|---|---|
| Domain | any(dns.domains[*] == "example.com") |
Host
Use this selector to match against only the hostname specified—for example, if you want to block only example.com but not subdomain.example.com.
| UI name | API example |
|---|---|
| Host | dns.fqdn == "www.example.com" |
Query Rtype
Use this selector to choose the DNS resource record type that you would like to apply policies against — for example, you can choose to block A records for a domain but not MX records.
| UI name | API example |
|---|---|
| Query Record Type | dns.query_rtype == "TXT" |
DNS Resolver IP
Use this selector to apply policies to DNS queries that arrived to your Gateway Resolver IP address aligned with a registered location. For most Gateway customers, this is an IPv4 AnyCast address and policies created using this IPv4 address will apply to all locations. However, each location has a dedicated IPv6 address and some Gateway customers have been supplied with a dedicated IPv4 address — these both can be used to apply policies to specific registered locations.
| UI name | API example |
|---|---|
| DNS Resolver IP | any(dns.resolved_ip[*] == 198.51.100.0) |
Resolved IP
Use this selector to filter based on the IP addresses that the query resolves to.
| UI name | API example |
|---|---|
| Resolved IP | any(dns.resolved_ips[*] == 198.51.100.0) |
Source IP
Use this selector to apply DNS policies to a specific source IP address that queries arrive to Gateway from — for example, this could be the WAN IP address of the stub resolver used by an organization to send queries upstream to Gateway.
| UI name | API example |
|---|---|
| Source IP | dns.src_ip == 198.51.100.0 |
Location
Use this selector to apply DNS policies to a specific location or set of locations.
| UI name | API example |
|---|---|
| Location | dns.location in {"location_uuid_1" "location_uuid_2"} |
Content Categories
Use this selector to apply DNS policies to traffic directed to specific content categories.
| UI name | API example |
|---|---|
| Content Categories | not(any(http.request.uri.content_category[*] in {1})) |
Security Categories
Use this selector to block traffic directed to specific security categories.
| UI name | API example |
|---|---|
| Security Categories | any(http.request.uri.category[*] in {1}) |
Authoritative Nameserver IP
Use this selector to match against the IP address of the authoritative name server IP address.
| UI name | API example |
|---|---|
| Authoritative Nameserver IP | dns.authoritative_ns_ips == 198.51.100.0 |
Operators
Operators are the way Gateway matches traffic to a selector. Matching happens as follows:
| Operator | Meaning |
|---|---|
| is | exact match, equals |
| is not | all except exact match |
| in | in any of defined entries |
| not in | not in defined entries |
| matches regex | regex evaluates to true |
| does not match regex | all except when regex evals to true |
Actions
Just like actions in HTTP policies, actions in DNS policies allow you to choose what to do with a given set of elements. You can assign one action per policy.
These are the action types you can choose from:
Allow
Policies with Allow actions allow DNS queries to reach destinations you specify within the Selector and Value fields. For example, the following configuration allows DNS queries to reach domains we categorize as belonging to the Education content category:
| Selector | Operator | Value | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content Categories | In | Education | Allow |
Block
Policies with Block actions block DNS queries to reach destinations you specify within the Selector and Value fields. For example, the following configuration blocks DNS queries from reaching domains we categorize as belonging to the Adult Themes content category:
| Selector | Operator | Value | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content Categories | In | Adult Themes | Block |
Override
Policies with Override actions allow you to respond to all DNS queries for a given domain to another destination. For example, you can provide a custom response IP of 1.2.3.4 for all queries to
www.example.com with the following policy:
| Selector | Operator | Value | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hostname | Is | 1.2.3.4 |
Override |
SafeSearch
SafeSearch is a feature of search engines that helps you filter explicit or offensive content. When you enable SafeSearch, the search engine filters explicit or offensive content and returns search results that are safe for children or at work.
You can use Cloudflare Gateway to enable SafeSearch on search engines like Google, Bing, Yandex, YouTube and DuckDuckGo. For example, to enable SafeSearch for Google, you can create the following policy:
| Selector | Operator | Value | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domain | Is | google.com |
SafeSearch |
YouTube Restricted Mode
Similarly, you can enforce YouTube Restricted mode by choosing the Youtube Restricted action. YouTube Restricted Mode is an automated filter for adult and offensive content built into YouTube. To enable Youtube Restricted Mode, you could set up a policy like the following:
| Selector | Operator | Value | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNS Domain | Is | youtube.com |
YouTube Restricted |
This setup ensures users will be blocked from accessing offensive sites using DNS.
Custom block page
When choosing the Block action, toggle the Display custom block page setting to respond to queries with a block page, and to specify the message you want to display to users who navigate to blocked websites. If disabled, Gateway will respond to blocked queries with 0.0.0.0. For more information, see the dedicated documentation on
customizing the block page
.