Deploy cloudflared in Azure
The purpose of this guide is to walk through some best practices for accessing private resources on AWS by deploying Cloudflare’s lightweight connector, cloudflared.
We will walk through how to initialize a service on a Linux VM in Azure, and route to it from another VM running cloudflared. This deployment guide does not take into account routing beyond basic security groups and default VPCs.
Prerequisites
- Navigate to the Zero Trust Dashboard and create a Cloudflare Zero Trust account.
- Enroll an end-user device into your Cloudflare Zero Trust account.
Create your environment
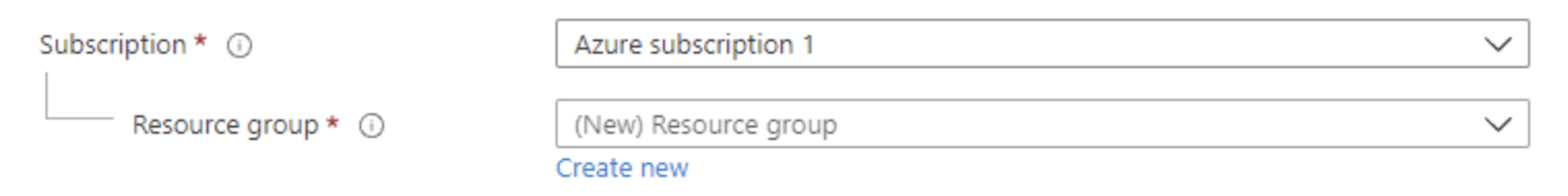
Make sure you sign up for Azure and create a new subscription.
-
First, create your first resource group.
-
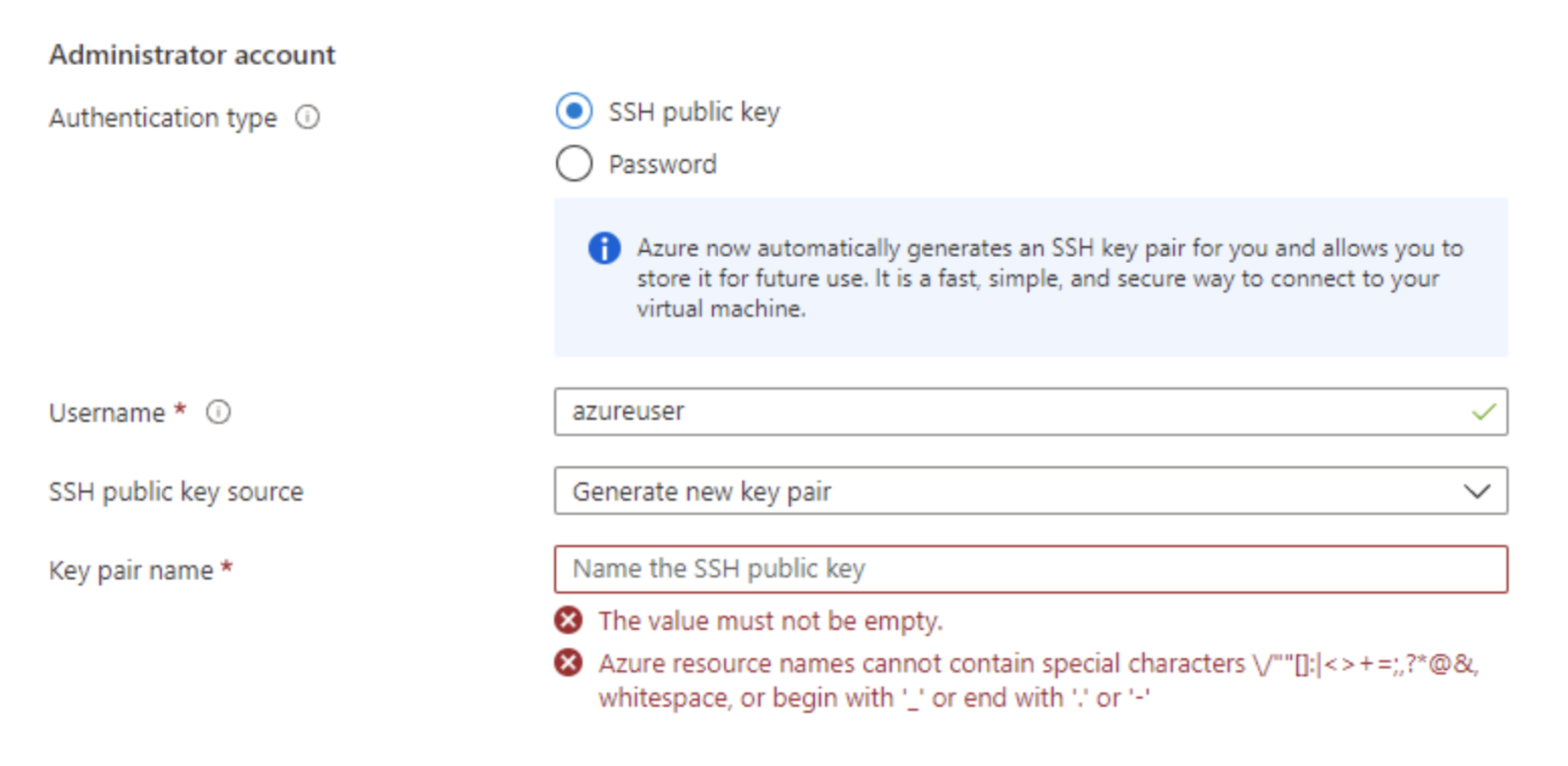
In addition, create your first keypair as well. You will be using the keypair to SSH into your Virtual Machine.
-
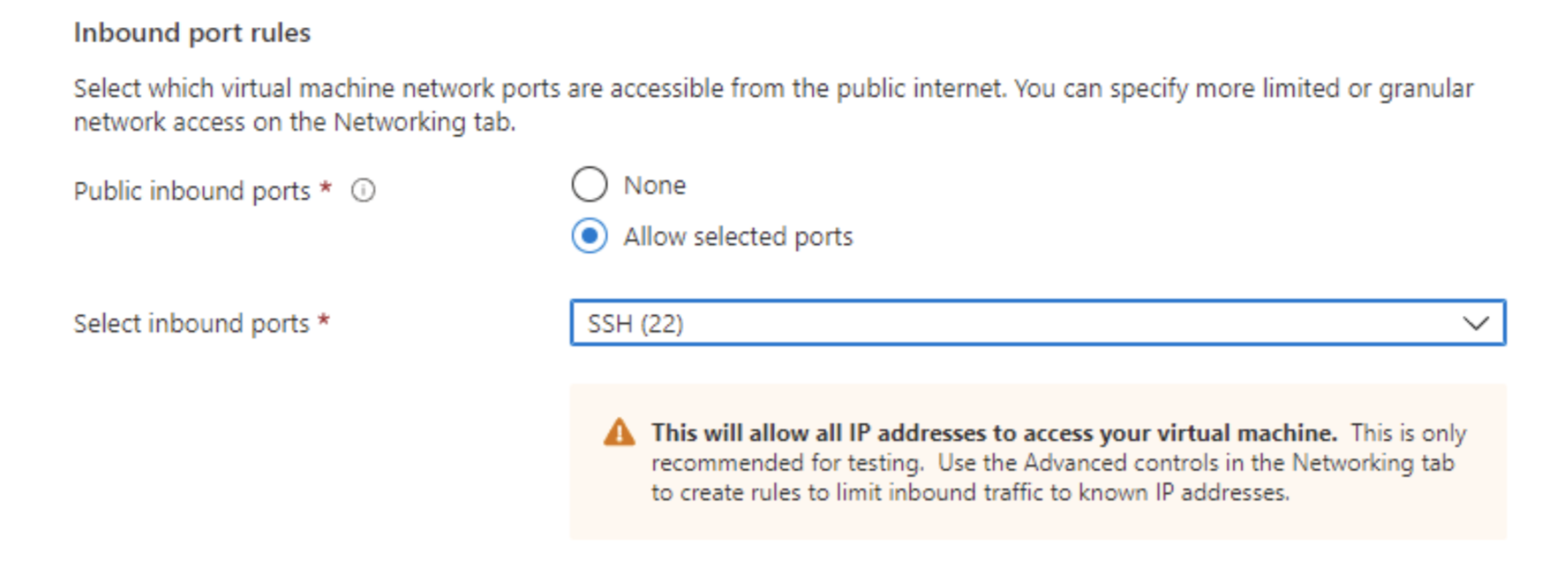
Next, define your inbound and outbound ports to the VM. If these ports are not configured properly, the solution will not function as intended. For testing purposes, we will leave access open.
Create two Ubuntu 20.04 LTS VMs, and make sure you record their internal IP addresses. Azure by default uses the 10.0.0.0/8 subnet.
Deploy cloudflared
-
SSH into your AWS instance using the command line.
cd Downloadsssh -i <private key path> azureuser@20.115.124.241 -
Run
sudo suto gain full admin rights to the Virtual Machine. -
Install
cloudflaredon your instance. In this example, we are running a Debian-based instance, so download the Debian build ofcloudflared:wget https://github.com/cloudflare/cloudflared/releases/latest/download/cloudflared-linux-amd64.debdpkg -i cloudflared-linux-amd64.deb -
Run the following command to authenticate
cloudflaredwith your Cloudflare account. The command will launch a browser window where you will be prompted to log in with your Cloudflare account and pick any zone you have added to Cloudflare.$ cloudflared tunnel login -
Create a tunnel.
$ cloudflared tunnel create Azure-01
Complete tunnel configuration
-
Make a directory for your configuration file.
mkdir /etc/cloudflaredcd /etc/cloudflared -
Build a configuration file. Before moving forward and entering vim, copy your Tunnel ID and credentials path to a notepad.
vim config.yml -
Type
ito begin editing the file and copy-paste the following settings in it.tunnel: <Tunnel ID/name> credentials-file: /root/.cloudflared/<Tunnel ID>.json protocol: quic warp-routing: enabled: true logfile: /var/log/cloudflared.log #cloudflared to the origin debug loglevel: debug #cloudflared to cloudflare debug transport-loglevel: info -
Press
spaceand then type:xto save and exit. -
Run
cloudflaredas a service.
cloudflared service install
systemctl start cloudflared
systemctl status cloudflared
Next, visit the Zero Trust dashboard and ensure your new tunnel shows as active. Optionally, begin creating Zero Trust policies to secure your private resources.